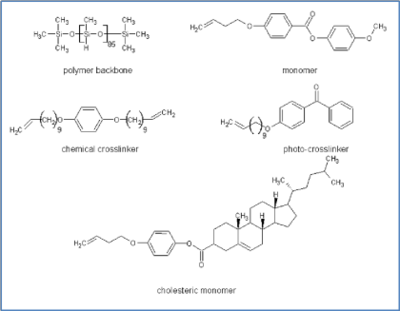
Cholesteric LCE films have narrow reflection bands that can be adjusted by stretching the material. When stretched,
the pitch, or distance between cholesteric layers is changed, shifting the reflection band of the LCE film,
as seen in the picture to the left. Varying the amount of the cholesteric molecules in the LCE,
allows control over the initial reflection band. These materials can be used for mirroless lasing applications
(ref. Adv. Mat. 2001(13), 2001. p 1069)
F. Brommel and S. Krause from Prof. Finkelmann's group
provided training for material preparation
This material may be prepared either by spin casting or photo-crosslinked in a cell. When made in a cell, the glass is coated with a sacrificial layer and is photo-crosslinked. When spin cast, the material is made using a chemical crosslinker.
- Chemical synthesis
- Mixture preparation
- Cell loading or spin casting
- Release from cell
- Characterization
Reaction progress can be monitored by UV-VIS spectroscopy, with the actual size and morphology of the Au NR checked by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM).