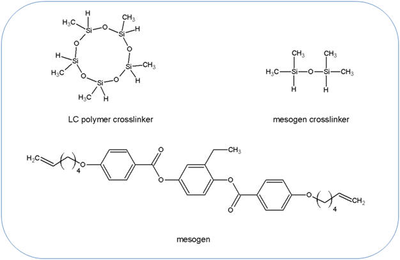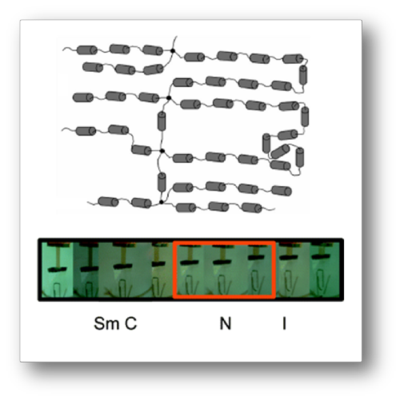
Main chain liquid crystal elastomer's (MCLCE) are composed of end to end linked LC mesogens that form
a linaer LC polymer chain. The LC polymers are cross-linked to each other to form the MCLCE. This
differs from side chain LCE (SCLCE) which utilize a linear siloxane polymer. The structure of a MCLCE is shown
in the picture to the left, where the mesogens are represented by grey cylinders, polymer chain
to chain cross-links by black dots, and links between mesogens by short wavy lines. This type of connectivity
allows MCLCE to undergo a dramatic changes in dimension, approaching 500%.
The photograph below illustrates the contraction of an LCE as it is heated to the isotropic phase transition.
The materials may be prepared by spin casting method using either chemical or photo-crosslinking methods
to establish the polymer network. (ref. Macromolecules
2008, (41) p 3098
Andrija Lebar & Felicity Brömmel provided instruction for preparation of chemically
&
photo-crosslinked MCLCE
This material may be prepared either by spin casting or photo-crosslinked in a cell. When made in a cell, the glass is coated with a sacrificial layer and is photo-crosslinked. When spin cast, the material is made using a chemical crosslinker.
- Chemical synthesis
- Mixture preparation
- Cell loading or spin casting
- Release from cell
- Characterization
Reaction progress can be monitored by UV-VIS spectroscopy, with the actual size and morphology of the Au NR checked by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM).